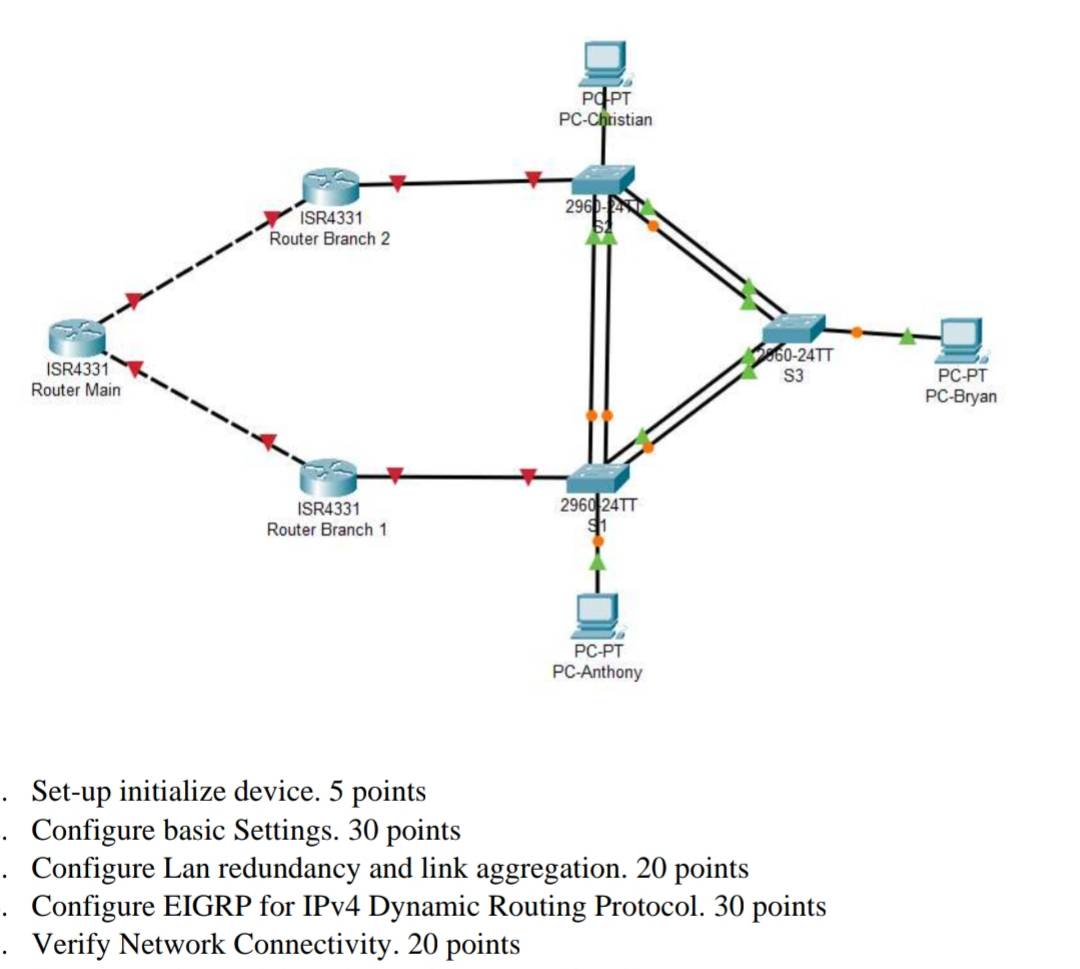
1. Set-up initialize device. 5 points
2. Configure basic Settings. 30 points
3. Configure Lan redundancy and link aggregation. 20 points
4. Configure EIGRP for IPv4 Dynamic Routing Protocol. 30 points
5. Verify Network Connectivity. 20 points
Sure! Let's go through each of the sections one by one.
1. Set up initialize device (5 points):
To initialize a device, you'll need to perform some basic tasks such as setting an IP address, setting up hostname, and configuring passwords. Here are the steps you can follow:
- Connect to the device using a console cable or a terminal emulator like PuTTY.
- Enter the privileged EXEC mode by typing "enable" and enter the enable password if prompted.
- Enter global configuration mode by typing "configure terminal".
- Set the hostname using the command "hostname [hostname]".
- Configure an IP address on the management interface using the command "interface [interface_name]" followed by "ip address [ip_address] [subnet_mask]".
- Set a default gateway using the command "ip default-gateway [gateway_address]".
- Lastly, secure your device by setting passwords for different modes using the "enable secret" and "line console 0" commands.
2. Configure basic settings (30 points):
To configure basic settings, you'll need to perform tasks such as setting up VLANs, configuring interfaces, and enabling protocols. Here are some steps you can follow:
- Create VLANs using the "vlan [vlan_id]" command in global configuration mode.
- Assign interfaces to VLANs using the "interface [interface_name]" command followed by "switchport mode access" and "switchport access vlan [vlan_id]" commands.
- Configure IP addresses on interfaces using the "interface [interface_name]" command followed by "ip address [ip_address] [subnet_mask]".
- Enable routing on the device using the "ip routing" command.
- Configure dynamic routing protocols like OSPF or EIGRP using the appropriate commands in global configuration mode.
3. Configure LAN redundancy and link aggregation (20 points):
To configure LAN redundancy and link aggregation, you'll need to implement techniques such as Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and link aggregation using EtherChannel. Here are some steps you can follow:
- Enable STP using the "spanning-tree mode [mode]" command in global configuration mode.
- Configure EtherChannel by bundling multiple physical interfaces into a single logical interface using the "interface port-channel [channel_number]" command followed by "interface [interface_name]" and "channel-group [channel_number] mode [mode]" commands.
4. Configure EIGRP for IPv4 dynamic routing protocol (30 points):
To configure EIGRP for IPv4, you'll need to follow these steps:
- Enter global configuration mode by typing "configure terminal".
- Enable EIGRP using the "router eigrp [AS_number]" command.
- Configure the network to participate in EIGRP using the "network [network_address] [wildcard_mask]" command.
- Adjust other EIGRP parameters such as metric values, timers, and authentication if required.
5. Verify network connectivity (20 points):
To verify network connectivity, you can use various troubleshooting commands such as "ping", "traceroute", and "show" commands. Here are some examples:
- Use the "ping [destination_ip_address]" command to check if you can reach a specific IP address.
- Use the "traceroute [destination_ip_address]" command to display the path taken by packets to reach the destination.
- Use the "show ip route" command to display the routing table and check if the routes are correctly learned.
Remember to practice these configurations on networking devices like Cisco routers or switches using tools like Packet Tracer or physical hardware if you have access to it. These steps should help you get started, but don't hesitate to reach out if you have any specific questions or need further assistance!