MORE INFO >>
DRTCP is
not a ρá†ch, but a shortcut (GUI interface) into your registry. It does not enter
anything by itself.
 TCP Receive Window
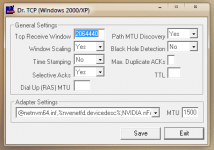
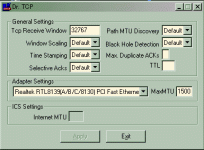
TCP Receive Window: This is where you set RWIN (RcvWindow). RWIN is the single most important tweak. Raising RWIN from default (8760 for Win95/98/98SE/NT and 17520 for WinME/2K/XP) can greatly improve download speeds. Why? Here is my kindergarten analogy: Default RWIN for broadband is like having a tiny straw in a thick milk shake, only so much so fast can get through the straw (line). By putting a larger straw (higher RWIN) in that same thick shake, you allow more shake (data) to come through faster, to a point that is. After there is no more improvement, shake (data) can start spilling all over (packet loss). So the key is to find an RWIN that fits your line just right. This is
blank before changing from default.
The formula for finding your "ideal" RWIN is to take your latency (average ping time in ms x 1.5), multiply that by your advertised (download) speed and divide that by 8.
Note: If setting RWIN below 8192, try using
even multiples of MSS.
Windows Scaling: 65535 is the highest RWIN you can use without Windows Scaling being turned on. Simply put, Scaling is needed to enter any number higher than 65535. However, you must also have the updated vtcp.386 ρá†ch (WinME/2K/XP does not need a ρá†ch). Relax, though; most users do not need to go higher than 65535. Windows Scaling
"Defaults" to off (same as No).
Time Stamping: The need for Time Stamping seems to be in question, at least with RWIN under 65535. If you have a line where latency varies a lot, or a "long fat pipe" (for example, pure satellite connection), then Time Stamping should be beneficial, so experiment with it. Time Stamping
"Defaults" to off (same as No).
Selective Acks: Selective Acks improve throughput (speed) on lines that tend to lose packets by retransmitting
only packets that were lost, if any.
"Defaults" to on (same as Yes) in Win98/98SE/ME/2K/XP and is N/A in Win95/NT.
Path MTU Discovery: This feature automatically sets your MTU (maximum transmission unit) to what type of line you have (dial-up (576), broadband 1492-1500). This is the size of packets you can receive. The highest MTU that one can have is 1500. For users with PPPoE connection software, it's 1492 and lower. Without PPPoE, it should default to 1500.
"Defaults"to on (same as Yes) in Win98/98SE/ME/2K/XP/NT and is N/A in Win95.
Black Hole Detection: Black Hole Detection discovers routers on the WEB that cause MTU Discovery to work sub-optimally.
"Defaults" to off (same as No) in Win95/98/98SE/ME/2K/XP.
Max. Duplicate ACKs: This function allows for faster retransmission of packets (information) when packet loss is encountered.
"Defaults" to blank, where blank stands for 3 in Win98/98SE/ME, 2 in WinNT/2K/XP and is N/A in Win95.
TTL: Time To Live (TTL) is the amount of hops (servers) that a transmission of packets will take before all packets are lost. If you were receiving packets from 20 hops away, and TTL was set to 19 or less, all packets would be lost before they reach you. Not a speed tweak.
"Defaults" to blank, where blank stands for 32 in Win95 and 128 in Win98/98SE/ME/2K/XP.
Adapter settings: This is where you set your MTU. Use the drop-down menu to find your NIC (Ethernet card).
If you do not know which adapter you should set, please ask. Do not set them all the same. (Note: If your MTU is 1500 by
default, it will be blank in DRTCP.) Also, only physical NICs supported for XP, no dial-up adapters.
Note: DRTCP
defaults to showing the dial-up adapter. This has
nothing to do with the other settings. It does
not matter which adapter is visible when setting anything except MTU. Also, upon reboot, the dial-up adapter will be showing
regardless of which adapter's MTU was set.
ICS Settings: Internet MTU is set when Internet Connection Sharing (a Microsoft program) is enabled and being used on your PC. This is where 2 or more PCs share the same Internet connection, though only one can surf at a time. ICS MTU should match that of the PC. This is grayed out if ICS is not being used (not ready for Win2K/XP).
Also: By right clicking on the logo and choosing "About," you will find information about the version of Windows you use.
Great, so what should you set all of these to? Most users can leave all of them at
Default (surprise!) except for RWIN, as this has been determined to be best most of the time, thus being
"Default." After making any changes, click Save, then Exit and then
reboot (restart) your PC. Use the
Tab button on your keyboard to move about DRTCP.
If you do not reboot, the settings will not "take."
DRTCP recommended by
Cisco.